Software development
Both microcontrollers are programmed using PlatformIO in VSCode using C++ language.
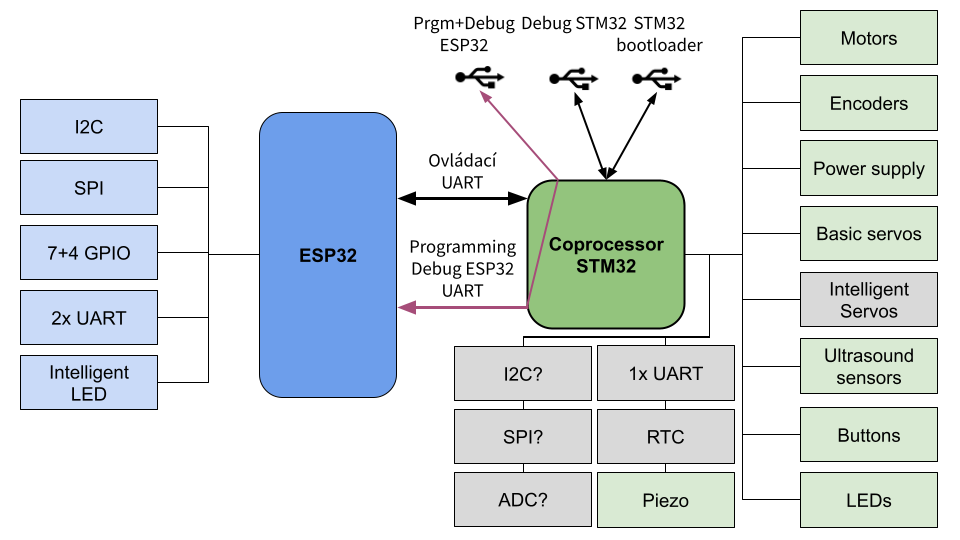
STM32
The software for STM32 is located in fw directory.
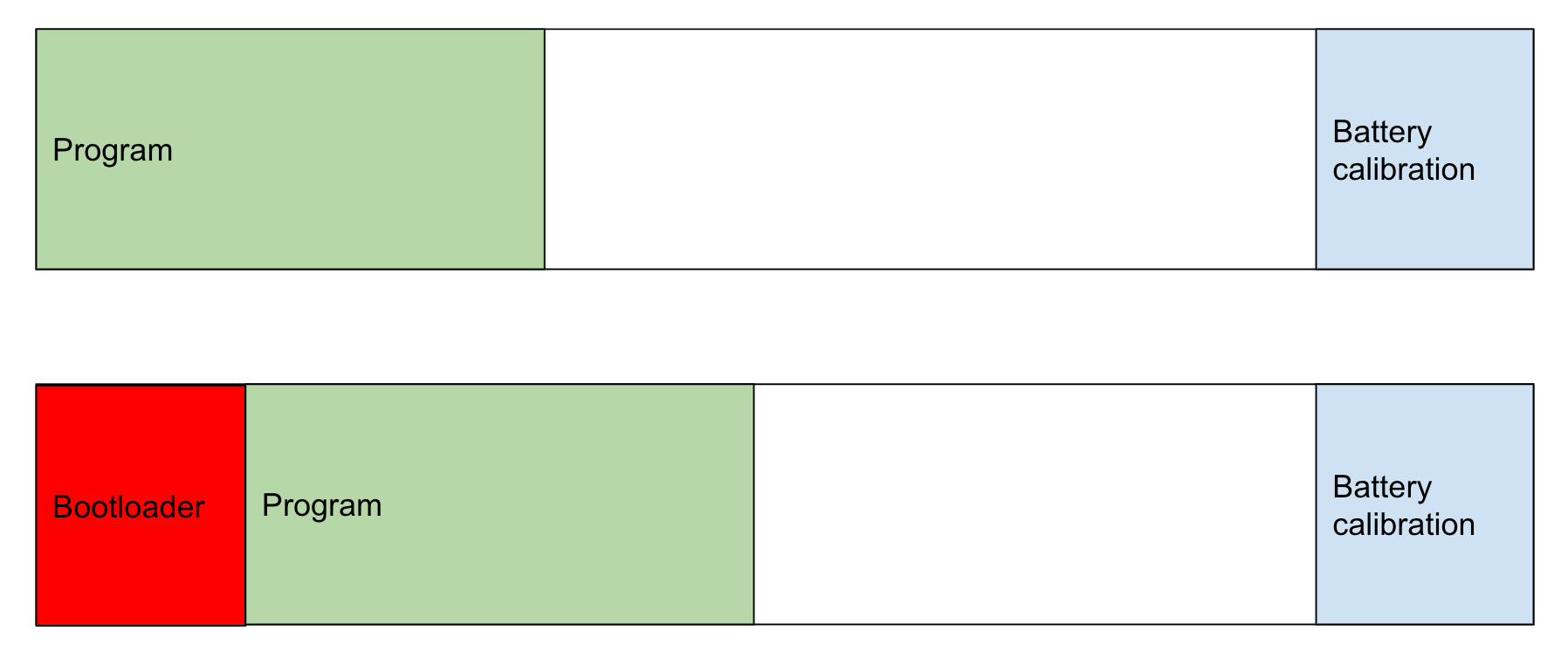
STM32 uses our bootloader, which is based on sboot_stm32.
The Czech manuals are in these presentations: - RBCX - RBCX firmware
Bootloader installation
RBCX might work without bootloader, but it is not recommended. Thanls to the bootloader, you can program STM32 without STLink programmer and program ESP32 directly trough USB-C in RBCX.
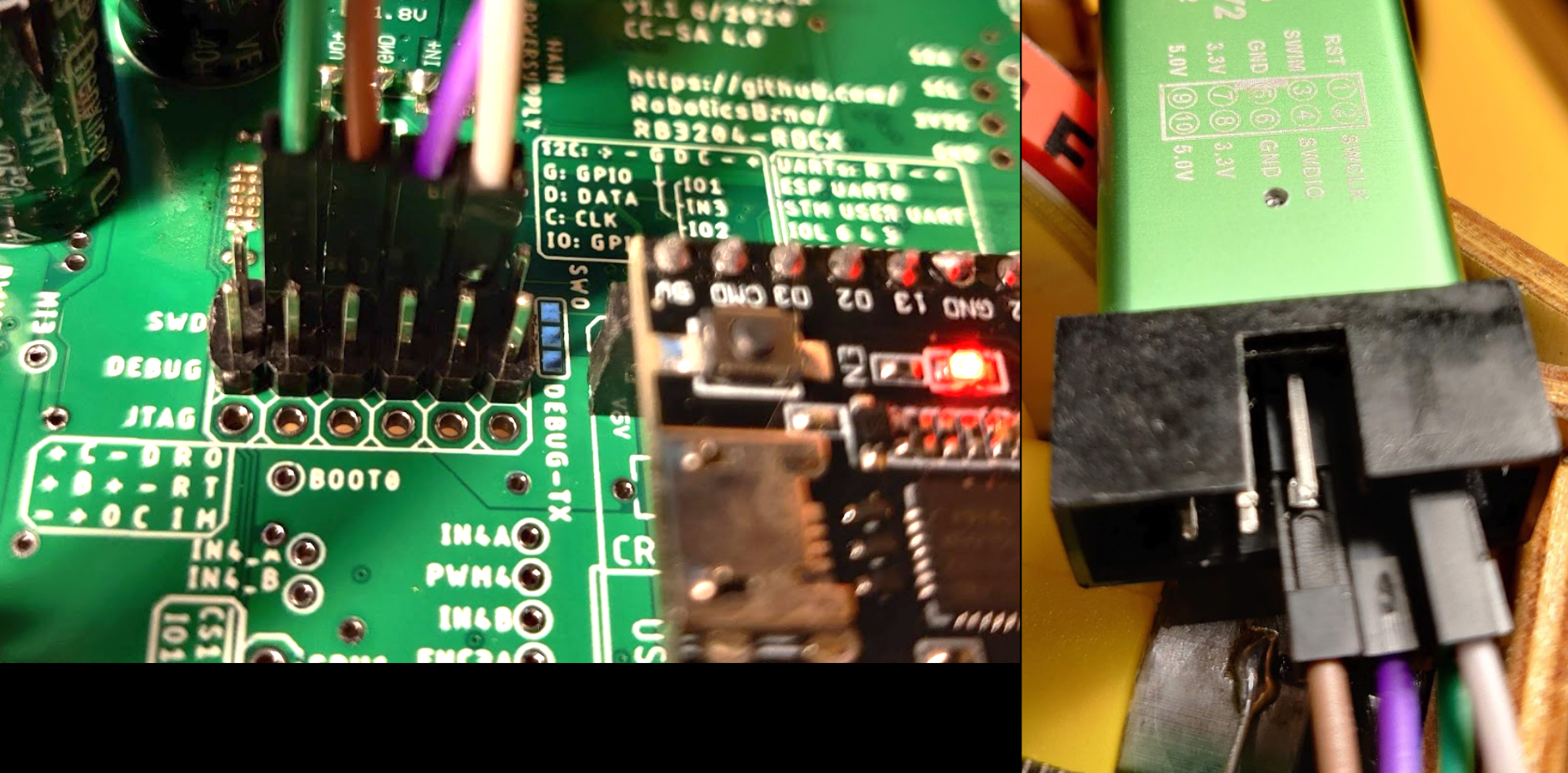
- you need STLink programmer
- connect STLink programmer to the board→
- C → SWCLK
- -→ GND
- D → SWDIO
- R → RST
- +→ 3.3V (optional, if you want to power the board from STLink)
- !! If STLink is not connected to the computer, STM32 is in a reset state !!
-
clone
https://github.com/RoboticsBrno/sboot_stm32 apt-get install stlink-tools make gcc-arm-none-eabi git- flash prebuilt bootloader
st-flash --reset --format ihex write prebuilt/rbcx_v11/firmware.hex - compile and flash firmware
make prerequisites && ./rbcx_build_v11.sh && make program
Firmware installation
Firmware for STM32 is located in fw/rbcx-coprocessor directory.
RBCX might be programmed using STLink programmer or using USB-C connector.
STLink development
In VSCode - PlatformIO, you have to change the environment to hw*_stlink.
This setup supports debugging. Just press F5 or Debug button in VSCode.
USB C development
If you want to use USB-C connector for programming STM32, you need to press DOWN button (B2) on the board during the boot.
In default mode, USB-C connector is used for communication with ESP32.
To enable Debug output from STM32, you have to press LEFT button (B3) on the board during the boot. This will add virtual debug serial port to the USB-C connector.
STM32 will create two virtual COM ports (one for STM32 and one for ESP32).
In VSCode - PlatformIO, you have to change the environment to hw*_sboot.
This setup does not support debugging (use STLink programmer for debugging).
ESP32
The library for ESP32 is in RB3204-RBCX-library repository. Examples for the Robotka, which is a robot based on RBCX, are in robotka-examples repository.
Programming ESP32
STM32 behaves like "FTDI" on dev kit, so you can program ESP32 using USB-C connector.
- Controls boot pins on ESP32 according to RTS/DTR.
- It supports faster UART than ESP32 DevKit (faster programming)
- ESP32 DevKit cannot be programmed via its own USB while plugged into RBCX
ESP32 and STM32 communication
ESP32 and STM32 communicate via UART (baud 921600)
Microcontrollers are communicating using Protocol Buffers (Protobuf). Protobuf messages are defined in RB3204-RBCX-coproc-comm repository.
Commands
"Run motor at 50%", "Battery voltage is 6802mV", "Reset the board"
Protocol: Protobuf + COBS + small header
0x00, <length>, <data>
Keepalive - when ESP32 does not respond, it is reset, STM32 turns off peripherals
Installation and usage
- clone
https://github.com/RoboticsBrno/RB3204-RBCX-coproc-comm - install protobuf compiler
apt-get install protobuf-compiler - install nanopb generator
pip3 install nanopb==0.4.4 - edit
rbcx.protofile - compile protobuf messages using
./generate.sh - commit and push changes to GitHub
- change GIT hash in FW and RBCX library to the latest commit hash